Bone Loss Is Accelerated by Which of the Following
Bone formation is occurring more rapidly than bone breakdown. The anatomic limits set by the dense cortical plates of the alveolus during anterior teeth movement could be regarded as orthodontic walls It seems that the pre-existing alveolar bone loss involving fenestration or dehiscence is common in the anterior mandibular teeth.
During your childhood adolescence and early adult years the rate at which new tissue is deposited is greater than the rate at which it is withdrawn.

. Accelerated loss 10 loss at either the total hip or femoral neck n 299 184. Ratings 100 4 4 out of 4 people found this document helpful. This preview shows page 28 - 31 out of 47 pagespreview shows page 28 - 31 out of 47 pages.
Pat FitzGerald November 1 2019 Primary osteoporosis is associated with the normal loss of estrogen following the menopause as well as age. Frailty is defined as having. This rapid bone loss can be prevented by estrogen or hormone replacement 9 10.
Tap card to see definition. Accelerated Postmenopausal Bone Loss Due to Gonadal Sex Steroid Deficiency Menopause is associated with onset of rapid bone loss in most women. This is thought to be due to decreased ovarian function leading to decreased estrogen secretion.
Which of the following medications may prevent the accelerated phase of bone loss within the first 5 years following the onset of menopause. Volume 21 Issue 1 July 1997 Pages 79-82. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google.
Which of the following is a characteristic of bone. The purpose of this prospective study was to monitor the bone mineral density BMD of the lumbar spine and contralateral femoral neck in the first year following an osteoporosis. A The bone matrix is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts.
Close Log In. Investigation of pharmacologic or other interventions in the first critical year following a hip fracture may potentially blunt this accelerated rate of bone loss and lessen the risk of subsequent fractures. Investigation of pharmacologic or other interventions in the first critical year following a hip fracture may potentially blunt this accelerated rate of bone loss and lessen the risk of subsequent fractures.
A fenestration is a window of bone loss that places the exposed root. Bone loss was particularly pronounced during intervals that included an incident fracture of the vertebrae elbow humerus clavicle hip and pelvis. Remember me on this computer.
We retrospectively characterized areal bone mineral density aBMD change from the year 7 to year 14 exam in three categories. Enter the email address you signed up with and well email you a. Click card to see definition.
These findings mirror the accelerated bone loss and spontaneous fractures recently described following discontinuation of treatment with. A prospective longitudinal study. High alcohol intake and smoking can also contribute to bone loss.
Which of the following happens after menopause as a result of decreasing estrogen. Calcium and vitamin D deficiency may increase the possibility of suffering from accelerated bone mass loss. In addition high alcohol intake is associated with increased bone loss falling and fractures in older men.
B stronger and heavier. Accelerated bone mineral loss following a hip fracture. Womens reserve of bone minerals is lower than mens to begin with.
The average older woman with normal bone density loses about 13 of her bone density in 10 years or about 13 per year. Which of the following contribute to functional decline and. Accelerated bone loss was isolated to the 2-year period that included the fracture.
Which of the following factors contributes to middle-aged womens accelerated loss of bone density compared to that of men. Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates could be. Click again to see term.
Which one of the following is occurring at the point labeled with the arrow. The loss of BMD from the femoral neck in the year following a hip fracture is more that 5 times that. This accelerated bone loss was not observed during the 2 years before or 2 years after the fracture interval.
Bone breakdown exceeds bone formation due to normal aging. Which of the following are nonhormonal agents that act directly to inhibit bone reabsorption. Expected loss.
Bone is continuously reconstructed by a process called bone remodeling in which old bone is destructed by osteoclasts and subsequently replaced with new bone by osteoblasts 1 3An imbalance between resorption and formation is often a central feature of metabolic bone diseases such as osteoporosis in which excessive resorption. Every day bone tissue is added and withdrawn from your bones. Peak bone mass has been reached.
Accelerated bone loss and increased post-fracture mortality in elderly women and men. Author links open overlay panel DR. This accelerated rate of loss can have drastic consequences in an elderly population already exhibiting osteopenia and propensity to fall.
Tap again to see term. The disease osteomalacia causes calcium loss from the skeleton which would result in bones that are A more resistant to compression. Furthermore we show that OPGFc treatment results in accumulation of osteomorphs that are able to reassemble rapidly into large activated osteoclasts upon OPGFc withdrawal resulting in bone loss.
The results of this study indicate that there is an accelerated rate of loss of bone mineral in the year following a hip fracture particularly from the contralateral proximal femur and that this loss is independent of the patients ability to return to full community ambulation.

In The Long Term A Single Implant Can Be More Aesthetic And Easier To Keep Clean Than A Bridge Gums Can Recede Around In 2022 Keep It Cleaner Periodontitis Implants

Easy Health Options Osteoporosis On The Rise For Both Men And Women How To Reduce Your Risk Osteoporosis Tlc Diet Health Options
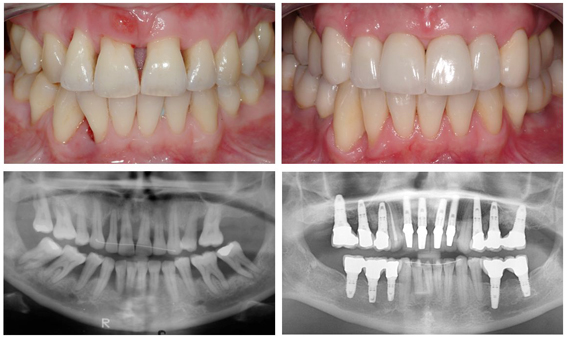
Rebuilding Bone Loss In Gums Blog Advanced Dentistry
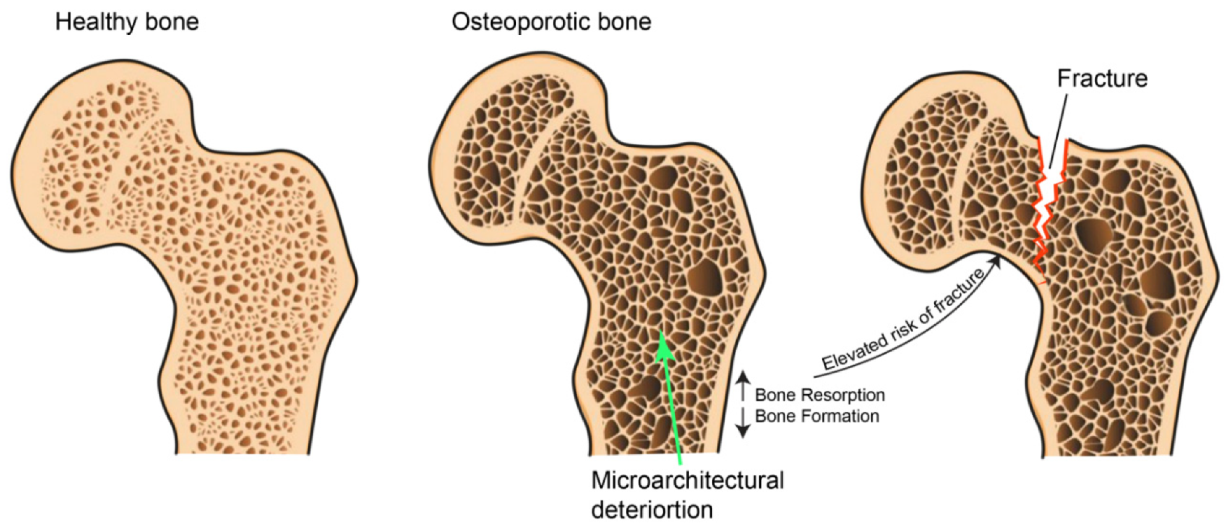
Ijms Free Full Text Platelet Features And Derivatives In Osteoporosis A Rational And Systematic Review On The Best Evidence Html

No comments for "Bone Loss Is Accelerated by Which of the Following"
Post a Comment